Query definition
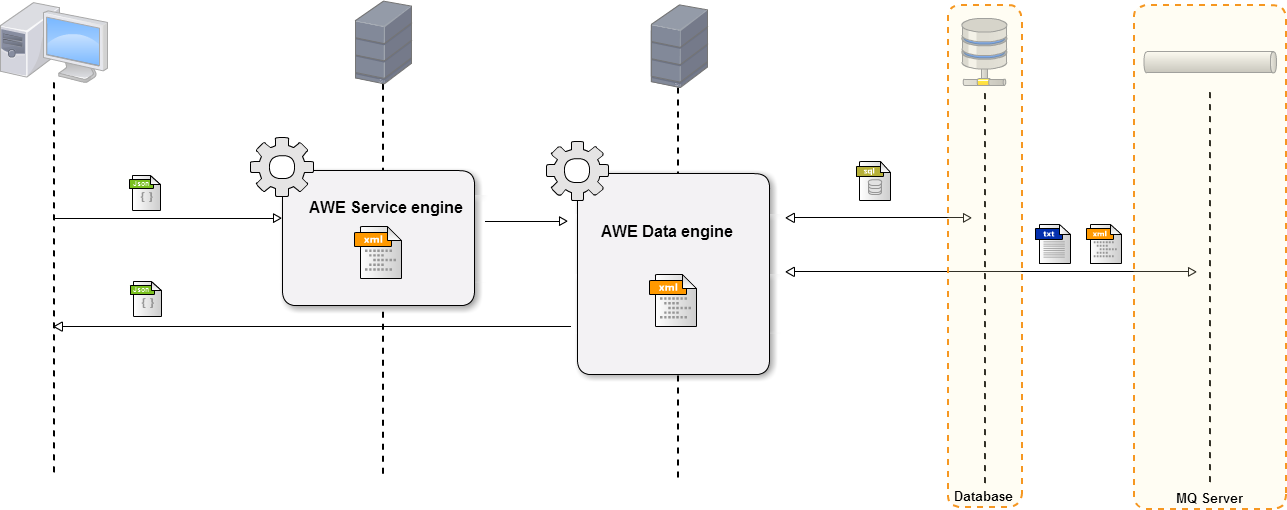
The AWE query engine is used for querying data on external systems. It works as an interface.
Note: All queries are defined in the queries.xml file at global folder. View project structure for more info.
SQL query
This section describes how database queries are handled with the AWE query engine.
XML sql structure
The complete sql query structure is the following:
<!-- Example sql query -->
<query id="[Query Id]" cacheable="[Cacheable]" distinct="Distinct" managed-pagination="Pagination" post-process="Post processed">
<table id="[Table id]" schema="[Schema name]" alias="[Table alias] query="[Subquery]"/>
<field id="[Field id]" table="[Table field]" alias="[Alias field]"/>
...
<field id="[Field id]" table="[Table field]" alias="[Alias field]"/>
<field variable="[Variable id]"/>
<constant value="[Constant value]" type="INTEGER"/>
<computed format="[Format]" alias="[Alias] transform="[Transform]"/>
...
<computed format="[Format]" alias="[Alias] transform="[Transform]"/>
<compound alias="[Compoun alias]">
<computed format="[Format]" alias="[Alias]"/>
...
<computed format="[Format]" alias="[Alias]"/>
</compound>
<join type="[Type join]">
<table id="[Table id]" alias="[Table alias]"/>
<and>
<filter left-field="[Field]" left-table="[Table]" condition="[Condition]" right-field="[Counterfield]"
right-table="[Countertable]"/>
...
<filter left-field="[Field]" left-table="[Table]" condition="[Condition]" right-variable="[Variable]"/>
</and>
</join>
...
<union type="[union_type]" query="[Union subquery]"/>
<where>
<and>
<filter left-field="[Filter field]" table="[Filter table]" condition="[Condition]" right-variable="[Variable]" optional="[Filter Optional]"/>
<filter left-field="[Field 1]" table="[Filter table]" condition="[Condition]"
right-field="[Field 2]" right-table="[Table 2]" ignorecase="[Ignorecase]" trim="[Trim]"/>
<filter left-field="[Field]" table="[Filter table]" condition="[Condition]" right-query="[Subquery]"/>
<or>
... (more filters or filter groups)
</or>
... (more filters or filter groups)
</and>
<or>
... (more filters or filter groups)
</or>
</where>
<variable id="[Variable id]" type="[Variable Type]" name="[Variable name]" optional="[Optional]"/>
... (More <variable>)
<group_by field="[Group field]" table="[Group table]" />
... (More <group_by>)
<order-by field="[Order field]" table="[Order table]" type="[Order type]"/>
... (More <order-by >)
<totalize function="[Totalize function]" label="[Label]" field="[Totalize field]" style="[Totalize style]">
<totalize_by field="[Totalize by field]"/>
... (more totalize by fields)
<totalize_field field="[Totalize field]"/>
... (more totalized fields)
</totalize>
</query>
Global Sql query structure
To simplify the development of queries, not all elements are required.
| Elemento | Uso | Varias instancias | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| query | Obligatorio | No | Outlines the query. Also describes the kind of query (service, queue, etc) |
| table | Obligatorio | Si | The table or table list over which the query is performed |
| field | Obligatorio | Si | Describes the column of the table |
| computed | Opcional | Si | Computed elements are used for retrieving query fields from other columns (field) |
| compound | Opcional | Si | Compound elements are a computed list. Used for retrieving complex structures |
| join | Opcional | Si | Used to make joins between tables |
| union | Opcional | Si | Used to make unions between tables |
| where | Opcional | No | Where clause in sql query. It has the condition list of fields |
| having | Opcional | No | Having clause in sql query. It has the condition list of fields for functions |
| group-by | Opcional | Si | Group by clause in sql query |
| order-by | Opcional | Si | Order by clause in sql query |
| totalize | Opcional | Si | Used to totalize the query result |
| variable | Opcional | Si | Parameters passed from screens to query |
Query element
The query element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Obligatorio | String | Query identifier | Note: The id name must be unique |
| distinct | Opcional | Boolean | Used to return only distinct (different) values | By default is false |
| cacheable | Opcional | Boolean | Used to set a query as cacheable (in order to save data in memory and avoid executing the query again) | By default is false. Note: If you set a query as cacheable and there are subqueries, you must define on it the same variables that all subqueries have. |
| managed-pagination | Opcional | Boolean | To set a query as paginated (to load just the data in that specific page, not all query registries). Used to achieve high performance in queries with a very high number of records. | By default is false. Note: Use this parameter only in queries without totalize. |
| post-process | Opcional | Boolean | Launch or not the processing of the datalist that AWE performs, in order to to allow developers to do their own post processing | By default is true. Note: Only apply in service queries. For more info. see service query |
| public | Opcional | Boolean | Allows the query to run without the need to be logged | By default is false |
| enumerated | Opcional | String | The name of enumerate to fill the query | Note: Only applies in enumerated queries. For more info. see enumerated query |
| service | Opcional | String | The name of service to fill the query | Note: Only applies in service queries. For more info. see service query |
| queue | Opcional | String | The name of queue to fill the query | Note: Only applies in queue queries. For more info. see queue query |
SQL elements
The following elements are translated into a SQL clause. They are part of the standard SQL instructions:
Table element
The table element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Obligatorio | String | Name of the table | Note: Actual table name in data base |
| schema | Opcional | String | Schema of the table. It is used to set the user owner of table | Note: It is the actuala schema (user) name in data base |
| alias | Opcional | String | Alias of the table. It is used to temporarily rename a table or a column heading | |
| query | Opcional | String | Id of a subquery to be used as data source |
Subquery example
<query id="GetProcessedAccounting" distinct="true">
<field id="Name" alias="nameCol" table="a" />
<field id="Created_Date" alias="createdDateCol" table="a"/>
<field id="Type" alias="typeCol" table="a"/>
<field id="ddo.OperationsCol" />
<table id="ACCOUNTING" alias="a" />
<join type="LEFT">
<!-- Use Subquery -->
<table alias="ddo" query="GetProcessedAccountingDirectDebit"/>
<and>
<filter left-field="IdCol" left-table="ddo" condition="eq" right-field="Id" right-table="a" />
</and>
</join>
</query>
<!-- Define Subquery -->
<query id="GetProcessedAccountingDirectDebit">
<field id="Id" alias="idCol" table="a" />
<field id="Id" alias="OperationsCol" function="COUNT" table="a"/>
<table id="ACCOUNTING" alias="a" />
<join type="LEFT">
<table id="ADEUDO_OPERACION" alias="o"/>
<and>
<filter left-field="Accounting_Id" left-table="o" condition="eq" right-field="Id" right-table="a" />
</and>
</join>
<where>
<and>
<filter left-field="Accounting_Id" left-table="o" condition="is not null" />
</and>
</where>
<group-by field="Id" table="a"/>
</query>
Field element
The field element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Opcional | String | Name of field | Note: Actual column name of table in data base |
| table | Opcional | String | Table of the field | |
| alias | Opcional | String | Alias of the field. Used to describe the field | |
| noprint | Opcional | Boolean | Used to set a field as no printable. (Field value won't be loaded in the resultSet) | |
| transform | Opcional | String | Used to format the field value | Check out this for more info about transform attribute. |
| pattern | Opcional | String | Used in a number type field, defines the pattern to format the number | Check out this page for more info |
| translate | Opcional | String | Translates the output with an enumerated group identifier | Note: If the field value is equal to an enumerated value, outputs the enumerated label |
| function | Opcional | String | To apply an sql function to field | The possible values are defined in field functions |
| cast | Opcional | String | Changes the field format | The possible values are STRING, INTEGER, LONG, FLOAT and DOUBLE |
| query | Opcional | String | Query identifier to do a subquery | Note: The query id must exist, and table and id attributes will be ignored |
| variable | Opcional | String | A variable identifier to be used as field value | Note: If variable attribute is defined, table and id attributes will be ignored |
Note: The order in attribute reading for fields is the following: 1.
query2.variable3.id(andtableif defined)At least one of the previous attributes is required in a field.
Field functions
ABS: Absolute valueAVG: Values averageCNT: Count valuesCNT_DISTINCT: Count distinct valuesMAX: Max valueMIN: Min valueSUM: Sum valuesROW_NUMBER: Row numberRANK: Aggregation rankTRUNCDATE(not standard): Truncate dateYEAR: Retrieve year from dateMONTH: Retrieve month from dateDAY: Retrieve day from dateHOUR: Retrieve hours from dateMINUTE: Retrieve minutes from dateSECOND: Retrieve seconds from dateTRIM: Remove all spaces from both sides of the string
Transform attribute
These are the possible values for the transform attribute:
DATE: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a web date field (dd/MM/yyyy)DATE_MS: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a java date in milliseconds (for chart datetime axes)TIME: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a web time field (HH:mm:ss)TIMESTAMP: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a web timestamp field (dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss)TIMESTAMP_MS: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a web timestamp field with milliseconds (dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss.SSS)JS_DATE: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a javascript date field (for chart axes) (MM/dd/yyyy)JS_TIMESTAMP: Transforms the output field (Date/String) into a javascript timestamp field (MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss)GENERIC_DATE: Transforms the output field (String) from a date format defined onformat-fromto a date format defined onformat-toDATE_RDB: Transforms the output field (String) from an English RDF format (dd-MMM-yyyy) to a web date field (dd/MM/yyyy)ELAPSED_TIME: Transforms the output field (Long) from a long millisecond value to a localized string indicating the elapsed time (12h)DATE_SINCE: Transforms the output field (Date) into a localized string with the time difference from now (5 min ago)NUMBER: Transforms the output field as a number with a pattern. IMPORTANT:- When using this transform, the associated pattern has to have thousands separator. For instance: ###,###.00
- NEVER use this transform if the retrieved data is for a numeric component
- This transform is normally used when we want to show a numeric value in a visualization grid (columns without component)
NUMBER_PLAIN: Transforms the output field as a number with a raw pattern (without thousand separator). IMPORTANT:- When using this transform, the associated pattern must not have a thousands separator (e.g: ###.00)
- It can be used for numeric components and elements that have no component.
- This transform is normally used when we want to print numeric components and specify the number of decimals we want to see in the pdf file. Usually, the number of decimals of the pattern will match the "precision" defined in the number-format attribute of the numeric component.
BOOLEAN: Transforms the output field as a boolean value (true/false):TEXT_HTML: Transforms the output field into HTML text (to be showed in a HTML page)TEXT_PLAIN: Transforms the output field into plain text (to be showed inside a document)TEXT_UNILINE: Transforms the output field into a plain text without line breaksMARKDOWN_HTML: Transforms the output field from Markdown into HTML text (to be showed in a HTML page)DECRYPT: Decrypts a column value which is encrypted in the databaseARRAY: Splits a string value with the string inpatternattribute
Constant element
The constant element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alias | Opcional | String | Alias of the field. It used to describe the field | |
| noprint | Opcional | Boolean | Used to set a field as no printable. (Field value won't be loaded in resultSet) | |
| transform | Opcional | String | Used to format the field value | Read this for more info about transform attribute. |
| pattern | Opcional | String | Used in a number type field, defines the pattern to format the number | Read this page for more info |
| translate | Opcional | String | Translates the output with an enumerated group identifier | Note: If the field value is equal to an enumerated value, output the enumerated label |
| function | Opcional | String | To apply an sql function to field | The possible values are defined in field functions |
| cast | Opcional | String | Changes the field format | The possible values are STRING, INTEGER, LONG, FLOAT and DOUBLE |
| value | Obligatorio | String | A static value to be used as field value | |
| type | Opcional | String | Type of the value | The possible values are available here |
Operation element
The operation element allows to define operations between fields and will be resolved as SQL clauses:
<operation operator="[operator]" alias="[alias]">
<constant value="[constant value]" />
<field id="[field name]" table="[field table]" />
...
</field>
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| operator | Obligatorio | String | Operator of the operation | See operator attribute |
| alias | Opcional | String | Alias of field. It used to describe the field | |
| noprint | Opcional | Boolean | Used to set a field as no print. (Field value isn't loaded in resultset) | |
| transform | Opcional | String | Used to format the field value | See this for more info about transform attribute. |
| pattern | Opcional | String | Used in a number type value, defines the pattern to format the number | See this page for more info |
| translate | Opcional | String | Translates the output with an enumerated group identifier | Note: If the field value is equal to an enumerated value, output the enumerated label |
| function | Opcional | String | To apply sql function to field | The possible values are defined in field functions |
| cast | Opcional | String | Change the field format | The possible values are STRING, INTEGER, LONG, FLOAT and DOUBLE |
Operator attribute
These are the possible values for the operator attribute:
CONCAT: Concats some string fieldsREPLACE: Replace on the first field the string defined on second place with the string defined on third placeNULLIF: Sets null if equals to second operandCOALESCE: Given a set of fields, returns the first one which is NOT NULLADD: Sums two fields (+)SUB: Substracts two fields (-)MULT: Multiplies two fields (*)DIV: Divides two fields (/)MOD: Returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division, after one number is divided by another (called the modulus of the operation). (%)POWER: The first field is raised to the second field power (^)ROUND: Replacing a number with an approximate valueADD_SECONDS: Adds seconds to a date fieldADD_MINUTES: Adds minutes to a date fieldADD_HOURS: Adds hours to a date fieldADD_DAYS: Adds days to a date fieldADD_WEEKS: Adds weeks to a date fieldADD_MONTHS: Adds months to a date fieldADD_YEARS: Adds years to a date fieldDIFF_SECONDS: Calculates the difference in seconds between two datesDIFF_MINUTES: Calculates the difference in minutes between two datesDIFF_HOURS: Calculates the difference in hours between two datesDIFF_DAYS: Calculates the difference in days between two datesDIFF_WEEKS: Calculates the difference in weeks between two datesDIFF_MONTHS: Calculates the difference in months between two datesDIFF_YEARS: Calculates the difference in years between two datesSUB_SECONDS: Substracts seconds from a date fieldSUB_MINUTES: Substracts minutes from a date fieldSUB_HOURS: Substracts hours from a date fieldSUB_DAYS: Substracts days from a date fieldSUB_WEEKS: Substracts weeks from a date fieldSUB_MONTHS: Substracts months from a date fieldSUB_YEARS: Substracts years from a date field
Operation examples
Concatenated field: ("Pro" + pro.Nam + "-Mod" + mod.Nam) as parent
<operation operator="CONCAT" alias="parent">
<constant value="Pro" />
<field id="Nam" table="pro" />
<constant value="-Mod" />
<field id="Nam" table="mod" />
</field>
Add 1 to a field: (pro.Nam + 1) as parent
<operation operator="ADD" alias="parent">
<field id="Nam" table="pro" />
<constant value="1" type="INTEGER"/>
</field>
Round field with 2 decimals: 'round(column, 2)'
<operation operator="ROUND" alias="roundField">
<field id="Rate" table="User" />
<constant value="2" type="INTEGER"/>
</field>
Case element
The case element allows to generate a list of when clauses inside a field element. An else clause must be defined at the end of the case clause. It has the same attributes than a filter element plus some extra features:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alias | Opcional | String | Alias of field. It used to describe the field | |
| noprint | Opcional | Boolean | Used to set a field as no printable. (Field value isn't loaded in resultset) | |
| transform | Opcional | String | Used to format the field value | See this for more info about transform attribute. |
| pattern | Opcional | String | Used in a number type field, defines the pattern to format the number | See this page for more info |
| translate | Opcional | String | Translates the output with an enumerated group identifier | Note: If the field value is equal to an enumerated value, output the enumerated label |
| function | Opcional | String | To apply sql function to field | The possible values are defined in field functions |
| cast | Opcional | String | Changes the field format | The possible values are STRING, INTEGER, LONG, FLOAT and DOUBLE |
NEW!: As described on filter element,
left-operandandright-operandmust contain a node offield,constant,operationorcaseas well. Same case for thethenandelseelements.
NEW!: You can use multiple filters inside
whenclause usingandclause as described here.
Case examples
Case field:
CASE WHEN (Nam = "sunset") THEN 1 WHEN (Nam = "sunny") THEN 2 WHEN (Nam = "purple-hills") THEN 3 ELSE 0 END AS "value"
will be generated as:
<query id="testCaseWhenElse">
<table id="AweThm"/>
<case alias="value">
<when condition="eq">
<left-operand>
<field id="Nam"/>
</left-operand>
<right-operand>
<field variable="sunset"/>
</right-operand>
<then>
<constant value="1" type="INTEGER"/>
</then>
</when>
<when left-field="Nam" condition="eq" right-variable="sunny">
<then>
<constant value="2" type="INTEGER"/>
</then>
</when>
<when left-field="Nam" condition="eq" right-variable="purple-hills">
<then>
<constant value="3" type="INTEGER"/>
</then>
</when>
<else>
<constant value="0" type="INTEGER"/>
</else>
</case>
<variable id="sunset" type="STRING" value="sunset"/>
<variable id="sunny" type="STRING" value="sunny"/>
<variable id="purple-hills" type="STRING" value="purple-hills"/>
</query>
Case field:
CASE WHEN (Nam = "sunset" AND Thm = "summer") THEN 1 ELSE 0 END AS "value"
will be generated as:
<query id="testCaseWhenMultipleFilters">
<table id="AweThm"/>
<case alias="Nam">
<when>
<and>
<filter condition="eq">
<left-operand>
<field id="Nam"/>
</left-operand>
<right-operand>
<field variable="sunset"/>
</right-operand>
</filter>
<filter condition="eq">
<left-operand>
<field id="Thm"/>
</left-operand>
<right-operand>
<field variable="summer"/>
</right-operand>
</filter>
</and>
<then>
<constant value="1" type="INTEGER"/>
</then>
</when>
<else>
<constant value="0" type="INTEGER"/>
</else>
</case>
<variable id="sunset" type="STRING" value="sunset"/>
<variable id="summer" type="STRING" value="summer"/>
</query>
Over element
The over element allows to modelate SQL window functions. This element contains a field clause (field, constant, operation or case) and some of partition-by or order-by clauses.
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alias | Opcional | String | Alias of the field. Used to describe the field | |
| noprint | Opcional | Boolean | Used to set a field as no printable. (Field value won't be loaded in resultSet) | |
| transform | Opcional | String | Used to format the field value | See this for more info about transform attribute. |
| pattern | Opcional | String | Used in a number type value, defines the pattern to format the number | See this page for more info |
| translate | Opcional | String | Translates the output with an enumerated group identifier | Note: If the field value is equal to an enumerated value, output the enumerated label |
| function | Opcional | String | To apply an sql function to field | The possible values are defined in over functions |
| cast | Opcional | String | Changes the field format | The possible values are STRING, INTEGER, LONG, FLOAT and DOUBLE |
Over functions
AVG: Values averageCNT: Counts valuesCNT_DISTINCT: Counts distinct valuesMAX: Max valueMIN: Min valueSUM: Sum valuesFIRST_VALUE: First valueLAST_VALUE: Last valueLAG: LagROW_NUMBER: Row numberTRUNCDATE(not standard): Truncates date
Over examples
Over field:
SELECT MAX(date) OVER (PARTITION BY name ORDER BY position ASC) as `maxValue` FROM tableId
will be generated as:
<query id="testOver">
<table id="tableId"/>
<over alias="maxValue">
<field id="date" function="MAX"/>
<partition-by field="name"/>
<order-by field="position" type="ASC"/>
</over>
</query>
Join element
The join structure is the next one:
<query id="query">
...
<join type="[Type]">
<table id="[Table id]" alias="[Table alias]"/>
<and>
<filter left-field="[Join field 1]" left-table="[Table join 1]" condition="eq"
right-field="[Join field 2]" right-table="[Table join 2]" ignorecase="[Ignorecase]" trim="[Trim]"/>
</and>
</join>
... (more joins)
...
</query>
The join element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| type | Opcional | String | SQL join type | The possible values are: FULL, LEFT, INNER or RIGHT Note: Default value is INNER. To see more info about joins read this page |
Union element
The union structure is the next one:
...
<query id="query">
<union type="[Type]" query="[Union subquery]"/>
... (more unions)
</query>
...
The union element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| query | Obligatorio | String | Query id to combine the result | Note: The alias query must be exist |
| type | Opcional | String | Combines the result of two or more SELECT statements | Use ALL to allow duplicate values |
Where element
The where element structure is the following one:
<query id="WhereTest">
<table id="HISAweThm" />
<field id="hisact" alias="typ" />
<where>
<and>
<filter left-field="hisact" condition="eq" right-variable="top" />
<filter left-field="hisope" condition="ne" right-variable="ope" />
</and>
</where>
<variable id="top" type="INTEGER" value="1445" />
<variable id="ope" type="STRING" value="mgr" />
</query>
Having element
The having structure is the next one, is the same as where element:
<query id="HavTst" public="true">
<table id="HISAweThm" />
<field id="hisact" alias="typ" />
<field id="sum(1)" alias="act"/>
<group-by field="HisAct"/>
<having>
<and>
<filter left-field="sum(1)" condition="gt" right-variable="top" />
</and>
</having>
<variable id="top" type="INTEGER" value="1445" />
</query>
Filter element
The filter structure is as follows:
<filter left-field="[Field 1]" left-table="[Field table 1]" left-variable="[Variable Id]" condition="[Condition]" type="[Type]"
right-field="[Field 2]" right-table="[Field table 2]" right-variable="[Variable Id]" query="[Query Id]" ignorecase="[Ignorecase]" trim="[Trim]" optional="[Optional]"/>
NEW! Now you can define a
left-operandand aright-operandchildren to define the filters. These elements must containfield,constant,operation,caseoroverelements:
<filter condition="[Condition]" ignorecase="[Ignorecase]" trim="[Trim]" optional="[Optional]">
<left-operand>
<field id="[field name]"/>
</left-operand>
<right-operand>
<constant value="[static value]" type="[value type]"/>
</right-operand>
</filter>
The filter element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| left-field | Opcional | String | The name of a column | |
| left-table | Opcional | String | The name of the table that field belongs to | |
| left-variable | Opcional | String | The id of a variable | |
| type | Opcional | String | The type of values stored in columns being compared | NUMBER, DECIMAL_NUMBER, DATE, TIME, STRING (default) |
| condition | Obligatorio | String | The condition of the comparison | See comparison conditions |
| right-field | Opcional | String | The name of a column | |
| right-table | Opcional | String | The name of the table that right-field belongs to | |
| right-variable | Opcional | String | The id of a variable | |
| query | Opcional | String | The id of a query to compare (right side) | |
| ignorecase | Opcional | Boolean | If comparison should ignore case | true, false (default) |
| trim | Opcional | Boolean | If values should be trimmed before comparison | true, false (default) |
| optional | Opcional | Boolean | If this filter is checking versus a variable and the variable value is null, then remove this filter | true, false (default) |
Comparison conditions
eq: Equalsne: Not equalsge: Greater or equalle: Lower or equalgt: Greater thanlt: Lower thanin: First operand is in a list defined by second operand (subquery or variable list)not in: First operand is not in a list defined by second operand (subquery or variable list)is null: First operand is nullis not null: First operand is not nulllike: First operand contains some text of second operandnot like: First operand does not contain some text of second operandexists: For queries only, subquery contains valuesnot exists: For queries only, subquery doesn't contain values
Group by element
The group by element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | Obligatorio | String | Field alias to group the results | |
| table | Opcional | String | Table alias to group the results | |
| function | Opcional | String | Function to apply to the field | The possible values are defined in field functions |
Also, you can use CASE operation inside group-by.
Order by element
The order by element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| field | Obligatorio | String | Field alias to order the results | |
| table | Opcional | String | Table alias to order the result | |
| function | Opcional | String | Function to apply to the field | The possible values are defined in field functions |
| type | Opcional | String | Order direction | The possible values are DESC or ASC. By default is ASC |
| nulls | Opcional | String | Whether to sort the null fields | The possible values are FIRST or LAST. By default depends on database type |
Post-Process elements
The following elements are very powerful in order to generate results, but they are evaluated after the generated SQL clause, and may introduce some slowness on query retrieval. Have this in mind when using them when designing data retrieval on big queries.
Computed element
The computed element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alias | Obligatorio | String | Computed field output name | |
| format | Obligatorio | String | Used to insert another field alias as variables. It has the same syntax as the javascript eval element | (Ex. [code] - [description] will take the code field and concatenate it with the description field with a " - " string |
| eval | Opcional | Boolean | Evaluates computed format as expression | By defaul is false |
| nullValue | Opcional | String | Sets a value to null values in computed fields | Ex: nullValue="ZERO" set "ZERO" to null values |
| transform | Opcional | String | Used to format the computed value | See this for more info about transform attribute. |
| pattern | Opcional | String | Used in a computed with numeric value, defines the pattern to format the number | See this page for more info |
| translate | Opcional | String | Translates the output with an enumerated group identifier | Note: If the field value is equal to an enumerated value, output the enumerated label |
| label | Opcional | String | To use an international i18n label in the computed | Note: You can use i18n files (locales) |
Computed examples
<!-- Computed for add string "Prueba" to field Nam -->
<query id="QryEdiSug" cacheable="true">
<table id="AweThm"/>
<field id="IdeThm" alias="value" />
<field id="Nam" alias="name" />
<computed alias="label" format="Prueba - [name]"/>
<where>
<or>
<filter left-field="Nam" condition="like" right-variable="Nam" ignorecase="true"/>
</or>
</where>
<variable id="Nam" type="STRINGB" name="suggest" />
</query>
<!-- Using computed to get value of field "Value" as a label field -->
<query id="ProNamLst" service="ProFilLst" cacheable="true">
<field id="value" />
<computed format="[value]" alias="label" />
</query>
Compound element
The compound structure is the next one:
<compound alias="[Compound alias]">
<computed format="[Format]" alias="[Alias]"/>
<computed format="[Format]" alias="[Alias]"/>
...
</compound>
The compound element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alias | Obligatorio | String | Is the compound identifier | Note: The alias name must be unique in the query |
Compound examples
Use compound element to get complex output structures.
<!-- This compound get label and icon from many computeds-->
<query id="DbsLst" cacheable="true">
<table id="AweDbs"/>
<field id="IdeDbs" alias="IdeDbs" />
<field id="Als" alias="Als" />
<field id="Des" alias="Des" />
<field id="Act" alias="Act" />
<field id="Act" alias="ActTxt" translate="Es1Es0"/>
<compound alias="ActIco">
<computed format="GENERAL_STATUS_FA_[Act]" alias="icon"/>
<computed format="[ActTxt]" alias="label"/>
</compound>
</query>
Usage of the icon compound:
- The compound
aliasmust match the icon fieldidin the grid. - The computed element with the alias
iconcontains the icon to be set the the icon field. In this case, there is an enum with the icons identifier. - The computed element with the alias
labelcontains the string to be shown on mosue over.
<!-- This compound get label and value as [Nam] field from many computeds fields -->
<query id="ScrCnfLst" cacheable="true">
<table id="AweScrCnf" alias="scrCnf"/>
<field id="IdeAweScrCnf" table="scrCnf" alias="IdeAweScrCnf" />
<field id="IdeOpe" table="scrCnf" alias="IdeOpe" />
<field id="IdePro" table="scrCnf" alias="IdePro" />
<field id="Nam" table="scrCnf" alias="NamVal" />
<compound alias="Nam">
<computed format="[NamVal]" alias="value"/>
<computed format="[NamVal]" alias="label"/>
</compound>
<where>
<and>
<filter left-field="Act" left-table="scrCnf" condition="eq" right-variable="Act" optional="true"/>
</and>
</where>
<variable id="Act" type="INTEGER" name="CrtAct" />
</query>
Totalize element
The totalize structure is the next one:
<query id="query">
...
<totalize function="[Function]" label="[Label]" field="[Field]" style="[Style]">
<totalize-by field="[Totalize field]"/>
... (more totalize by fields)
<totalize-field field="[Totalize field]"/>
... (more totalized fields)
</totalize>
... (more totalize)
...
</query>
The totalize element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| function | Obligatorio | String | Function used to generate the total | The possible values are defined on aggregation functions |
| label | Obligatorio | String | Label of the text to appear on totalizer-field in totalized rows | |
| field | Obligatorio | String | Field where the totalizer label is going to be shown | |
| style | Obligatorio | String | Is the css style to set in grid wiget | The possible values are TOTAL or SUBTOTAL |
Totalize element has the following elements:
| Elemento | Uso | Varias instancias | Descripción |
|---|---|---|---|
| totalize-field | Obligatorio | Si | Has field attribute to set the field alias to apply the totalization |
| totalize-by | Obligatorio | Si | Has field attribute to set the field alias to group in the totalization and function attribute to define a specific aggregation function |
Aggregation functions for totalize
AVG: Values averageCNT: Counts valuesCNT_DISTINCT: Counts distinct valuesMAX: Max valueMIN: Min valueSUM: Sum valuesFIRST_VALUE: First valueLAST_VALUE: Last value
Totalize examples
<!-- Test matrix with totalizer -->
<query id="QrySitModDbsOrdTot" cacheable="true">
<table query="QrySitModDbsOrd" alias="TotLst"/>
<field id="IdeSitModDbs" table="TotLst" alias="IdeSitModDbs"/>
<field id="IdeSit" table="TotLst" alias="IdeSit"/>
<field id="NamSit" table="TotLst" alias="NamSit"/>
<field id="IdeMod" table="TotLst" alias="IdeMod"/>
<field id="NamMod" table="TotLst" alias="NamMod"/>
<field id="IdeDbs" table="TotLst" alias="IdeDbs"/>
<field id="Als" table="TotLst" alias="Als"/>
<field id="Ord" table="TotLst" alias="Ord" transform="NUMBER"/>
<totalize function="SUM" label="Subtotal" field="NamMod" style="SUBTOTAL">
<totalize-field field="Ord"/>
<totalize-by field="IdeMod"/>
</totalize>
<totalize function="SUM" label="Total" field="Als" style="TOTAL">
<totalize-field field="Ord"/>
</totalize>
</query>
Variable element
The variable element has the following attributes:
| Atributo | Uso | Tipo | Descripción | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | Obligatorio | String | Identifier of variable | Note: The id must be unique |
| type | Obligatorio | String | Variable type | The possible values are available here |
| name | Opcional | String | Variable name. It's the name of the component we are interacting with in the screen | Note: In some cases it might be useful to know the name of the criterion we are interacting with. If we define the variable as name="component", it will send the id of the criterion |
| value | Opcional | String | To define a static value of the variable | |
| session | Opcional | String | Variable is set by a session value | |
| property | Opcional | String | Variable is set by a property value | |
| optional | Opcional | Boolean | Flag to indicate if variable is optional. If the criterion configured in the variable could exist or not. If it is optional and does not exist, the query won't be executed. If it is not optional and the variable does not exist an error will be shown. | Note: It's not recommended to configure suggest type criteria as optional, because it might lead to misbehaviour |
Variable types
These are the possible variable types:
- STRINGL: a string with % at left side (for
LIKEoperator) - STRINGR: a string with % at right side (for
LIKEoperator) - STRINGB: a string with % at both sides (for
LIKEoperator) - STRINGN: a string that has
NULLwhen it's empty - STRING: a string that has "" when it's empty
- STRING_HASH: applies Sha 256 function to string variable
- STRING_ENCRYPT: applies encryptRipEmd160 function to string variable
- INTEGER: integer number
- FLOAT: float number (32 bits)
- DOUBLE: double number (64 bits)
- DATE: web date (
dd/MM/aaaa) - TIME: web time (
HH:mm:ss) - TIMESTAMP: web timestamp (
dd/MM/aaaa HH:mm:ss) - SYSTEM_DATE: Server Date (stored as date) (
dd/MM/aaaa) - SYSTEM_TIME: Server time (Stored as string) (
HH:mm:ss) - SYSTEM_TIMESTAMP: Server Date (stored as timestamp with milliseconds) (
dd/MM/aaaa HH:mm:ss.SSS) - NULL: To pass a
nullvalue - OBJECT: To define a variable as a java object
- CLOB: To define a variable as a big text file
- LIST_TO_STRING: Retrieve a list of values and manage them as a comma separated values in a string
- STRING_TO_LIST: Retrieve comma separated string and transforms it into a list of values
Special variables
There are a set of special variables which don't need to be declared as variable on the query and affects the behaviour of the results:
- lang: Makes translation (with
translate="XxxXxx"attribute) to use this language instead of the session one
Enumerated query
An enumerated query is a call to an enumerated group in the Enumerated.xml file.
It will not receive any input variables, and will return a list with two fields: value and label.
You can check out enumerate xml structure in this page
Xml enumerated structure
<!-- Example enumerated query -->
<query id="[Query id]" enumerated="[Id enumerated]" cacheable="[cacheable]">
<field id="[Field label]"/>
<field id="[Field value]"/>
</query>
Note: All enumerated are defined in the
Enumerated.xmlfile at global folder. View project structure for more info.
Ejemplos de enumerados
<!-- Enumerated YES:1|NO:0 -->
<query id="Es1Es0" enumerated="Es1Es0">
<field id="value"/>
<field id="label"/>
</query>
<!-- Enumerated YES:Y|NO:N -->
<query id="EsyEnn" enumerated="EsyEnn">
<field id="value"/>
<field id="label"/>
</query>
Service query
Special type of queries used to call services, either if they are java or web services. A service query is composed by input variables and output fields.
You can view services xml structure in this page
Note: All services are defined in the
Services.xmlfile at global folder. View project structure for more info.
Xml service structure
<query id="[Query ID]" service="[Service ID]" public="[Public]">
<field id="[Field Id 1]"/>
...
<field id="[Field Id n]"/>
<computed alias="[Alias]" format="[Format]"/>
...
<computed alias="[Alias]" format="[Format]"/>
<variable id="[Variable ID1]" type="[Variable type]" name="[Variable name 1]" />
...
<variable id="[Variable IDn]" type="[Variable type]" name="[Variable name N]" />
<order-by field="[Order field]" table="[Order table]" type="[Order type]" nulls="[Nulls first or last]"/>
</query>
IMPORTANT: The order of the fields in query.xml must be the same as defined in the service in Services.xml file
Service examples
- Example of java service:
Code of query xml
<!-- Encrypt text (Service encryptText) -->
<query id="GetEncTxt" service="SerEncTxt" cacheable="true">
<field id="value" />
<field id="label" />
<variable id="text" type="STRING" name="CrtTxt"/>
<variable id="phraseKey" type="STRING" name="CrtPhr"/>
</query>
Code of service xml
<service id="SerEncTxt">
<java classname="com.almis.awe.core.services.controller.AccessController" method="encryptText">
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="text" />
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="phraseKey" />
</java>
</service>
- Example of web service:
Code of query xml
<query id="BoCptMomLiqTyp" service="FmbBoCptMomLiqTyp">
<field id="value"/>
<field id="orp_des"/>
<field id="lab"/>
<field id="orp_ext"/>
<computed alias="label" format="[orp_des] - [lab] - [orp_ext]"/>
<variable id="FldIde" type="STRING" value="LiqTyp" optional="false"/>
<variable id="LiqTyp" type="STRING" name="LiqTyp" optional="false"/>
</query>
Code of service xml
<service id="FmbBoCptMomLiqTyp">
<web name="FmbBoCptMomLiqTyp" type="DATA">
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="FldIde" list="false"/>
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="LiqTyp" list="false"/>
</web>
</service>
Queue query
Special type of queries used to communicate with message queues. A queue query is composed by input variables and output fields.
You can view queues xml structure in this page
Note: All queues are defined in the
Queues.xmlfile at global folder. View project structure for more info.
Xml queue structure
<query id="[Query ID]" queue="[Queue ID]" public="[Public]">
<!-- Output parameters -->
<field id="[Field Id 1]"/>
...
<field id="[Field Id n]"/>
<computed alias="[Alias]" format="[Format]"/>
...
<computed alias="[Alias]" format="[Format]"/>
<!-- Input parameters -->
<variable id="[Variable ID1]" type="[Variable type]" name="[Variable name 1]" />
...
<variable id="[Variable IDn]" type="[Variable type]" name="[Variable name N]" />
</query>
Queue examples
- Example of queue query:
Code of query xml
<!-- Queues: Fill a criterion with a wrapper values -->
<query id="TstSynQueWrpTxt" queue="SynQueWrpTxt">
<!-- Input parameters -->
<variable id="CrtVen" type="INTEGER" value="4"/>
<variable id="CrtPue" type="INTEGER" value="2"/>
<!-- Output parameters -->
<field id="OutFld1" alias="value" />
<field id="OutFld2" alias="label" />
</query>
Code of queues xml
<!-- Queue retreive sync test with wrappers -->
<queue id="SynQueWrpTxt">
<request-message destination="AweReq" type="TEXT" selector="wrapper">
<message-wrapper type="XML" classname="com.almis.awe.core.wrappers.test.Casa"/>
</request-message>
<response-message destination="AweRes" type="TEXT">
<message-wrapper type="XML" classname="com.almis.awe.core.wrappers.test.Casa"/>
</response-message>
</queue>