awe-107 Services
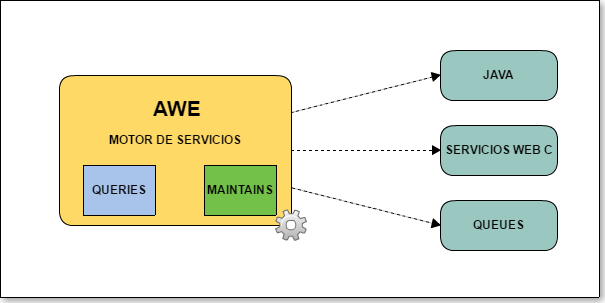
Services within AWE are useful to execute any kind of bussiness logic on the server side. It can execute Java or C code to do whatever task we want to.
Services are a kind of action, exposed on the client side as actions of type server where the query or maintain to be executed comes along with the service attribute (for queries) or <serve> element (for maintains).
The service engine is the one who redirects to the appropiate engine depending on the action type (data or maintain) as well as the service type (Java, C web services, message queues, ...)
For the service definition it is necessary to specify in global/services.xml file. The complete list of elements and attributes for services can be found in wiki🔗.
Development of a Java service
Java services are those used for Java code execution as Spring Beans. We can execute functions from the project as well as third party APIs. The only condition is that the java class has to be loaded in the classpath and has @Service annotation .
The specific attributes for Java services are documented here🔗.
- Example: To help to understand this tutorial we are going to develop a simple Java service where we will execute a method from one of our classes to fill in a criterion. The method will receive 2 parameters and will return as the result its concatenation.
Definition in global/services.xml
To develop the Java service with AWE it will be necessary to specify in services.xml the structure of the service.
<service id="MyJavaService">
<java classname="com.app.services.MyService" method="concat">
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="text1" />
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="text2" />
</java>
</service>
As you can see, our service has and identifier (MyJavaService). We told it to execute the method concat defined in class MyService whose complete path in classpath is com.app.services.MyService. Also, we have specified that this method will receive two parameters of type String called text1 and text2.
Service
Once the service is defined in the xml, we have to create the bean component class and method to execute. For this, it is recommended to have a logic layer as a controller and from there call the method we want to execute defined in the manager. This way, we can modify the controller layer without impacting the bussiness logic from the manager, making the code more maintainable.
Following this recommendation, we are going to create the Servicios class as a controller.
IMPORTANT: This class may extend
ServiceConfigclass to be able to access the context of the application.
package com.app.services;
// Imports
@Service
public class MyService extends ServiceConfig {
/**
* Concat two strings
* @param text1 text1
* @param text2 text2
* @return concated text
*/
public ServiceData concatenar(String text1, String text2) {
// Define serviceData
ServiceData serviceData = new ServiceData();
String concatResult = text1 + text2;
// Set data as array of label and value. Also you can build DataList and set it.
serviceData.setData(new String[] { concatResult, concatResult });
return serviceData;
}
}
IMPORTANT: As can be seen, a method that receives two strings and returns a
ServiceDataobject has been defined. All services must return this AWE object. This object, among other things, has theDatalistproperty where all the data to be returned is stored.
As we can see, the method concat returns the object ServiceData with the result of the concatenation of two parameters. In this example, the information to be returned was done by creating an array two elements long (label and value) that have the same value.
** Note:** This would be one of the many way to return information in AWE. Another way could be creating a
Datalistobject with the information relative to rows and columns and adding it to theServiceDataobject that must be returned.
Development of a web service
Web services are a kind of special service used to invoke C functions throught the web service provided by the ALU (ALmis Utilities) library.
The specific attributes for the Web ALU services are documented here🔗.
- Example: As we did with Java services, we are going to develop a C service that concatenates two Strings to fill in a criterion.
Definition in global/services.xml
The first thing we have to do is define the structure of the service inside of the services.xml file within the global folder, stating that it will be a web service (<web />).
<!-- Concatenate 2 strings -->
<service id="ConcatString">
<microservice name="alu-microservice" method="POST" endpoint="/data/CctStrDat">
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="texto1" />
<service-parameter type="STRING" name="texto2" />
</microservice>
</service>
As in the previous service, we have given an identifier name ConcatString. With the <web /> tag, we are specifying the type of service we are talking about.
In web service is necessary to indicate the name that will match the identifier defined in services.xml for this web service inside of folder webservices. It is important to point out that we have set the type attribute to DATA so we know that the service is going to return some (in this case, the string concatenation).
Definition in webservices/services.xml
This file will hold the proper definition of the web service. This file is used by the engine to convert the parameters and be able to build the SOAP request to the web service.
<!-- Return Concat String -->
<service name="CctStrDat" type="DATA" call="DoConcatString">
<param name="texto1" type="STRING"/>
<param name="texto2" type="STRING"/>
</service>
** Note:** it is important to note that the
nameattribute from the service element must have the same value as thenameattribute of the service defined inservices.xmlin global folder. Thecallattribute indicates the name of the function to be called in C (will be sent as a parameter).
Interface of service in xxxWbsFcn.c
Finally, we hace to define the functionality of the actual web service. For this, the file xxxWbsFcn.c has been created as a template.
/**************************************************************************************************/
/* %fname : ALUwbsGetSpeDtaPtr
* %synop : Web services specific function interface for data services
* %descrip : Web services specific function interface for data services
* %par :
* - Ide: Function identifier
* - Res: (out) Function Pointer
* %return : Error code (0: OK)
* %end
*/
int ALUwbsGetSpeDtaPtr (char *Ide, ALUwbsFcnDta *Ptr)
/**************************************************************************************************/
{
ERRdef;
*Ptr = NULL;
/* DATA FUNCTIONS */
/* Assign service name to function pointer */
/* SAMPLE:
* if (strcmp (Ide, "DatSrv1") == 0) { *Ptr = ALUwbsDatSrv1; }
* else if (strcmp (Ide, "DatSrv2") == 0) { *Ptr = ALUwbsDatSrv2; }
*/
/*-------- Get data-------*/
if (strcmp (Ide, "UsrChkPwd") == 0) { *Ptr = (ALUwbsFcnDta) BILwbsUsrChkPwd; }
...
else if (strcmp (Ide, "DoConcatString") == 0) { *Ptr = (ALUwbsFcnDta) DoConcatString; }
...
else {
ERRchk (ALUwbsGetDtaFcnPtr (Ide, Ptr));
if (*Ptr) {
goto ERRend;
}
}
ERRend:
ERRret;
}
/**************************************************************************************************/
/* %fname : DoConcatString
* %synop : Get the concat of two strings
* %descrip : Get the concat of two strings
* %par :
* - LdPar: Parameter List
* - Res: (out) Webservice response
* %return : Error code (0: OK)
* %end
*/
int BILwbsGetCor (void *LdPar,
wbsResDta *Res)
/**************************************************************************************************/
{
char Bas [COD_LENGTH];
int Cod = 0;
char *Ent,
*Dst,
*Sns;
ERRdef;
/* OUTPUT Initialization */
ERRchk(ALUwbsErrDtaIni(Res));
/* GET PARAMETERS */
Txt1 = (char *) DYNgbGetData (LdPar, DYNcbn (LdPar, "texto1"), 0);
Txt2 = (char *) DYNgbGetData (LdPar, DYNcbn (LdPar, "texto2"), 0);
/* Concat strings */
char *result = malloc(strlen(s1)+strlen(s2)+1);//+1 for the zero-terminator
//in real code you would check for errors in malloc here
strcpy(result, Txt1);
strcat(result, s2Txt2
ERRend:
/******** WEB SERVICE DATA MANAGMENT ********/
if (Res->ResLst) MMfree (Res->ResLst);
Res->ResLst = MMmalloc (char, sizeof (char ) * 50);
sprintf (Res->ResLst, "%d%", Cod);
/*********************************************/
/* ERROR Management */
ALUwbsErrDtaMgnErrCd (ErrCd, Res);
ERRret;
}
** Important:** Do not forget to create the header file
xxxWbsDef.h.
/**************************************************************************************************/
/* %finame : xxxWbsDef.h
* %acronyme :
* %synop : Header file for BilWbsFcn
* %descrip : Header file for BilWbsFcn
* %end
*/
/**************************************************************************************************/
...
int BILwbsUsrChkPwd (void *LdPar, wbsResDta *Res);
...